UVA Researcher Helps Develop Growth Mindset Program that Works in the 'Real World'
Curry News, December 2019







Affirming Independence: Exploring Mechanisms Underlying a Values Affirmation Intervention for First-Generation Students
Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 2016
Authors: Yoi Tibbetts, Judith Harackiewicz, Elizabeth Canning, Jilana Boston, Stacy Priniski, Janet Hyde
First-generation college students (students for whom neither parent has a 4-year college degree) earn lower grades and worry more about whether they belong in college, compared with continuing-generation students (who have at least 1 parent with a 4-year college degree). We conducted a longitudinal follow-up of participants from a study in which a values-affirmation intervention improved performance in a biology course for first-generation college students, and found that the treatment effect on grades persisted 3 years later.

Making Connections: Replicating and Extending the Utility Value Intervention in the Classroom
Journal of Educational Psychology, 2017
Authors: Chris Hulleman, Jeff Kosovich, Kenneth Barron, David Daniel
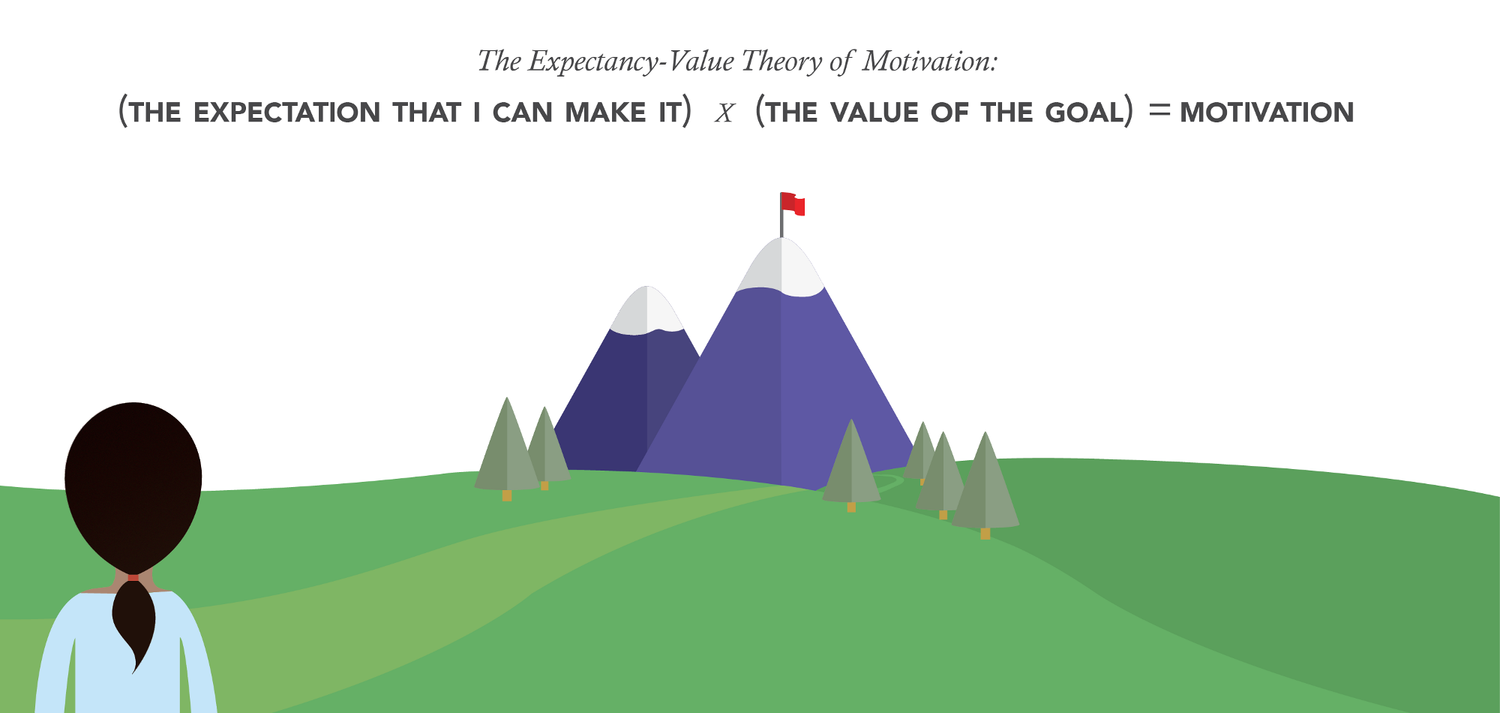
We replicated and extended prior research investigating a theoretically-guided intervention based on expectancy-value theory designed to enhance student learning outcomes (e.g., Hulleman & Harackiewicz, 2009). First, we replicated prior work by demonstrating that the utility value intervention, which manipulated whether students made connections between the course material and their lives, increased both interest and performance of low-performing students in a college general education course. Second, we extended prior research by both measuring and manipulating one possible pathway of intervention effects: the frequency with which students make connections between the material and their lives.
Utility Value Intervention with Parents Increases Students' STEM Preparation and Career Pursuit
PNAS, 2017
Authors: Christopher S. Rozek, Ryan C. Svoboda, Judith M. Harackiewicz, Christopher S. Hulleman, Janet S. Hyde
The need for students trained in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) jobs is growing rapidly in the United States, yet students do not enroll in the necessary courses to prepare for STEM careers. In a randomized controlled trial, parents in the utility–value intervention group received materials detailing the importance of STEM for their adolescents in high school. The intervention increased mathematics and science ACT scores and course-taking in high school. This greater high-school STEM preparation was associated, 5 y later, with increased STEM career pursuit. These findings suggest that educational policies should promote the personal relevance of high-school mathematics and science courses and involve parents in helping to promote STEM preparation and career pursuit.

Peer Victimization and Adolescent Adjustment: Does School Belonging Matter?
Authors: Stephanie Wormington, Kristen Anderson, Ashley Schneider, Kristin Tomlinson, Sandra Brown
Recent research highlights the role of peer victimization in students’ adjustment across a variety of domains (e.g., academic, social), but less often identifies potential mediating variables. In the current study, we tested for direct effects from peer victimization to adolescents’ academic behavior and alcohol use, as well as indirect effects through school belonging.

Using Design Thinking to Improve Psychological Interventions
Journal of Educational Psychology, 2016
Authors: David Yeager, Chris Hulleman, Gregory Walton
There are many promising psychological interventions on the horizon, but there is no clear methodology for preparing them to be scaled up. Drawing on design thinking, the present research formalizes a methodology for redesigning and tailoring initial interventions. We test the methodology using the case of fixed versus growth mindsets during the transition to high school.